Rio – The benefits of exercise outweigh the old view that it only provides weight loss and cardiovascular conditioning. They help prevent and fight various diseases such as cancer, diabetes, dementia, osteoporosis and infections. Behind all this force are at least 650 substances produced by skeletal muscles when they are exercised. It is so powerful that it can even improve the immune system’s response to the Covid-19 vaccination.
Some of these substances have been recently discovered and the function of only 5% of them is known, reveals a review of studies published in the scientific journal Frontiers in Physiology. It’s called The Role of Muscle Secretion in Health and Disease (The Role of Muscle Secretion in Health and Disease, in free translation), and it shows the latest in science in understanding the complex biochemistry of muscle. The name of muscle secretion is the group of substances produced by muscles.
What little has actually been discovered is astonishing scientists and paving the way for a more efficient use of physical activity in preventing and combating disease, as well as delaying aging. Active muscles help make your skin healthier.
More than strength and support, muscles are the balm factories for a good life. These are hormones, growth factors, immune system substances and a whole host of powerful proteins.
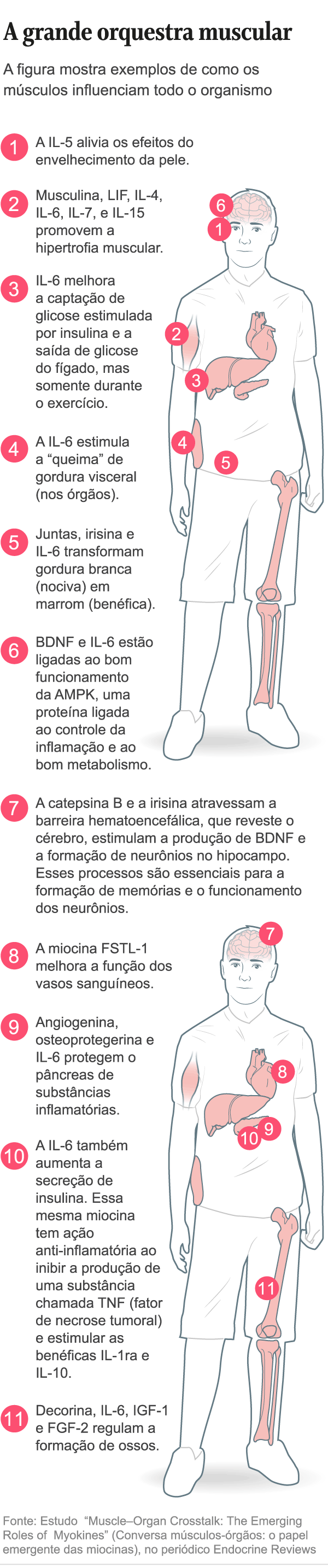
This plant is driven by the muscle contraction that occurs each time the muscle is exercised. It produces substances collectively called myokines. They connect muscles to other organs, such as the immune system, brain, liver, pancreas, bones, intestines, skin, adipose tissue (fat), and blood vessels. It is also essential for the hypertrophy, regeneration and functioning of the muscles themselves.
No wonder scientists recommend exercise for people with cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Taken together, approximately 700 skeletal muscles (the number ranges from 650 to 840, there is no consensus in the scientific literature) is the largest endocrine organ in the body, says sports medicine specialist Claudio Gil Araujo, MD, director of the Clinical Sports Medicine (Clinimex).
Muscles are the heaviest organ in the body, making up about 40% of the weight. But its biochemical functions are more important. They produce unique myokines, but they also make and release substances produced by other organs.
An example of the beneficial effects for the muscles you exercise comes from research recently published by Brazilian scientists, and is still in print. And research by researchers at the University of São Paulo and other institutions showed that physical activity improves the response to vaccination against Covid-19, even in people with weakened immune systems.
The scientists looked at the difference in response to CoronaVac in people with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. One of the study’s authors, Hamilton Ruschel, coordinator of the Research Group in Applied Physiology and Nutrition in the School of Physical Education and University of the South Pacific School of Medicine, explains that those who were physically active produced more antibodies than those who were sedentary. .
Everything works best when you do regular physical activity, your immune system, your cardiovascular system, your metabolism, your brain. Absolutely everything, ”emphasizes Roschel.
Our wonderful orchestra
When we do sports, the orchestra starts playing. The conductor is muscle contraction and myokinate musicians. They play in response to each other. composing a melody. The more physical activity, and thus muscle contraction, the more musicians play, release other substances, and the musical notes that set the body’s rhythm. A sedentary lifestyle is silence and disharmony, that is, disease.
Some myokines, for example, pick up blood glucose and lower blood glucose. It is a natural remedy for diabetes. Others respond to vasodilation, remodeling the endothelial matrix (the lining of the internal blood vessels), thereby reducing hypertension.
The exercise works on the morphology of the brain. The action is so profound that they act on microRNAs and thus help regulate protein synthesis. Regular exercise reduces inflammation, which is one of the great evils of modern life, says muscle physiologist Jose Cesar Rosa Neto, of the Immunology Metabolism Laboratory in the Department of Cell Biology and Development at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences at USP.
Muscles are stimulated by exercise, releasing substances with an anti-inflammatory effect. These are interleukins 4, 6, 10 and 13. And it was only relatively recently that science discovered that muscles, and not just immune cells, produce these substances.
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) has gained prominence in the pandemic, for its association with the exacerbation of Covid-19. In critically ill Covid-19 patients, the rate rises and leads to the dreaded cytokine storm (itself one of them), an inflammatory imbalance that may result in death.
Excessive intake of IL-6 is always a sign of a problem for Covid19 and other inflammatory diseases. But not when exercise comes into play. Rosa Netto says that during exercise, the level of IL-6 can increase 100 times. But it degrades the faster it increases. Meanwhile, it fights inflammation. It is as if IL-6 is bipolar. If it continues to rise, as is the case with Covid-19 and other diseases, it generates severe inflammation. On the other hand, high and short doses have the opposite and beneficial effect, they are an effective anti-inflammatory.
The relationship with IL-6 represents all the subtlety and complexity involved in the relationship between muscle and the rest of the body. An extensive relationship about which little is known. The number of myokines is estimated to be over 650, with millions of possible interactions. It is an orchestra that plays and renews itself every time a person exercises and contracts their muscles.
In this orchestra, the intensity and timing of the exercise set the tone, says Rosa Netto. Sometimes more time is needed, which is likely the case with most anti-inflammatory myokines.
allies against cancer
But in other cases, it’s the force that gets the right note. An example is interleukin-15, which has an antitumor effect. Muscle releases it when exposed to intense exercise. IL-15 activates the production of T-cell killers and T-lymphocytes. Cells of the immune system patrol the body for infected or defective cells (such as cancer cells) and kill them.
IL-15 makes killer lymphocytes more alert and efficient. One thing is true. Regular physical activity really improves immunity – Rosa Netto explains.
For some materials, it takes more time and severity. This is the state of BDNF, and it is necessary for neurons to survive and function properly. In order to release them, the calf muscles must be exercised. The people on the arms are not important in this particular case, notes Rosa Netto.
In general, muscles are the largest organ of our endocrine glands and are very easy to stimulate, just contracting. But one of the biggest challenges is figuring out the myokines release pattern – Rosa Netto confirms.
No movement, no health
If doing physical activity is good, lack of movement is bad. Moving at any level is critical. Physical activity is necessary to keep the body functions in balance.
“The body is like a new car. You can have a great model, but it will spoil if left in the garage,” says Roschel.
According to him, it is not necessary to practice digital influencers or necessarily go to the gym. The important thing is to move. It’s not necessary to set a specific time, but rather to increase the time devoted to physical activity within the daily routine, says Rosshel, who has a project looking at the most effective way to do this.
This is how humanity goes
Exercise attempts to compensate for the lack of regular physical activity in the pattern into which the human body has developed. The body was not made to stand still. get sick and die. Claudio Gil Araujo says Nature’s Factory model is to go fast. This is how humanity has proceeded for most of its journey that began more than 300,000 years ago.
But running, swimming, cycling, weight training, dancing, and a host of other activities act as palliatives in our age, when we spend most of our time sitting or lying down.
It will not be just decades of modern and sedentary lifestyle that will change the human being. No wonder a sedentary lifestyle is considered a disease – says Araujo.
Illusions and magic pills
Araujo and Rosa Neto both consider it unlikely that it would be possible to develop an exercise pill.
Muscles are activated in many ways, at different times, with variable reactions, and at different intervals and doses. Rosa Netto says it’s impossible to focus all this on a drug.
Scientists are unanimously agreed that exercise alone is a natural and powerful medicine against old and new diseases.

“Wannabe internet buff. Future teen idol. Hardcore zombie guru. Gamer. Avid creator. Entrepreneur. Bacon ninja.”