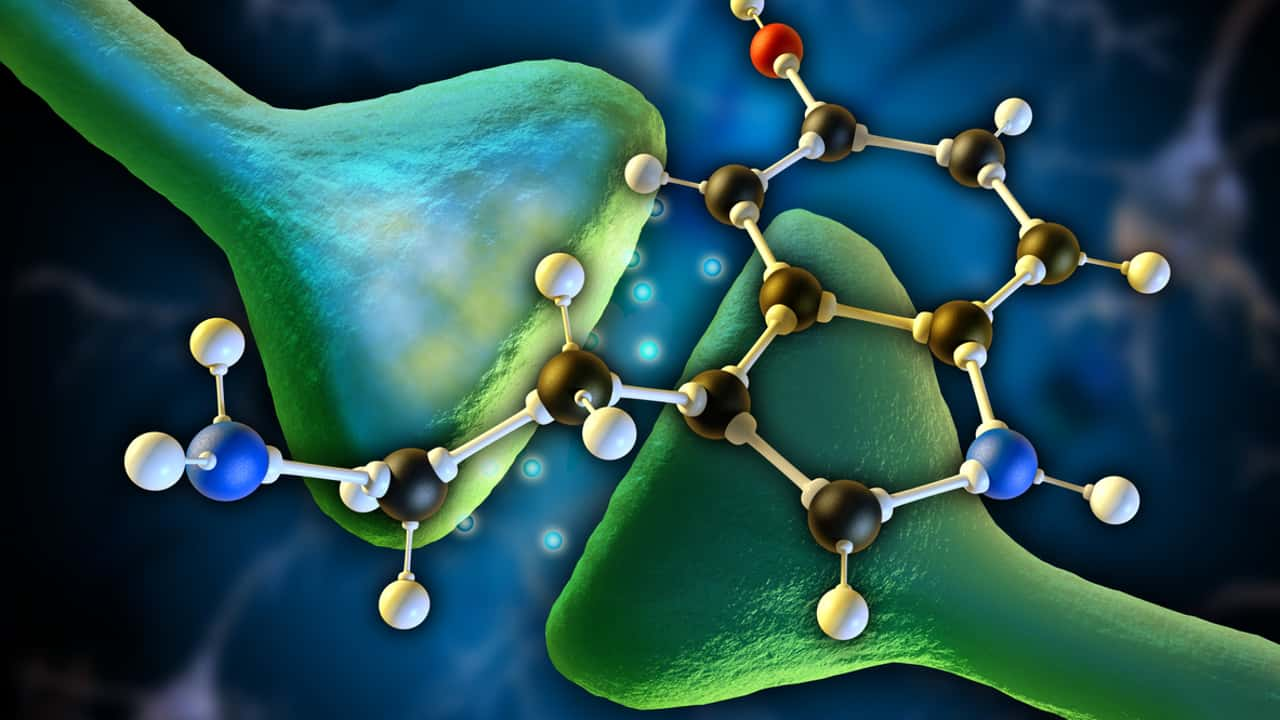
Serotonin, the so-called “happiness hormone,” is a neurotransmitter, a chemical that plays an essential role in communication between nerve cells (nerve cells) in the central nervous system. It can affect many bodily functions – but symptoms that affect the psyche are more common when there is a deficiency.
What are the functions of serotonin?
Serotonin is responsible for transmitting information between brain cells (neurotransmitter function). It also “moves” in the blood to control the functions of various organs (hormonal function).
It also affects many processes in the body and psyche – including mood and motivation control, sleep-wake rhythm and memory performance, as well as digestion, blood clotting, body temperature and pain perception. Overall, the release of serotonin in the brain promotes well-being, relaxation, and serenity.
Credits: Andreus/iStock
Typical symptoms of serotonin deficiency
Many symptoms of deficiency affect the psyche. The lack of calming and relaxing hormone effects, for example, leads to increased anxiety and internal restlessness.
These are the seven most common symptoms of serotonin deficiency:
- anxiety
- Depressive mood
- Internal voltage
- Irritability
- Lack of motivation
- Sleep disorders
- exhaustion
Physical symptoms of serotonin deficiency
In addition, serotonin deficiency can cause physical symptoms such as increased pain perception and changes in appetite. Headaches, migraines, increased premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and irritable bowel syndrome are also possible consequences.
It is important to remember that these symptoms can be caused by a variety of factors, and a diagnosis of serotonin deficiency or serotonin-related disorder should be made by a health care professional.
Evaluating levels of this hormone generally involves clinical examinations and evaluations.

“Wannabe internet buff. Future teen idol. Hardcore zombie guru. Gamer. Avid creator. Entrepreneur. Bacon ninja.”