There is a 27.5% chance of a deadly pandemic like COVID 19 occurring in the next 10 yearsAnd According to a study A company that specializes in predictive analysis of diseases at the population level in real time.
a Air Co., Ltd. , based in London, has stated that, based on its modeling, it has proven that this is the case The current risks, fueled by climate change, increased international travel, population growth and the threat posed by zoonotic diseases.
Zoonotic diseases
We refer to a disease or infection that occurs in animals and which, under certain conditions, can be transmitted to humans under normal conditions.
75% of new infectious diseases affecting humans are of animal origin, and on a planet with increasing pressure on the natural environment, these diseases are increasingly at risk.. HIV, Ebola, and COVID-19 are examples of this emerging danger.
The worst case scenario
According to Airfinity, In a worst-case scenario, an avian flu-like virus mutated to allow human-to-human transmission could kill at least 15,000 people in one day in the UK alone..
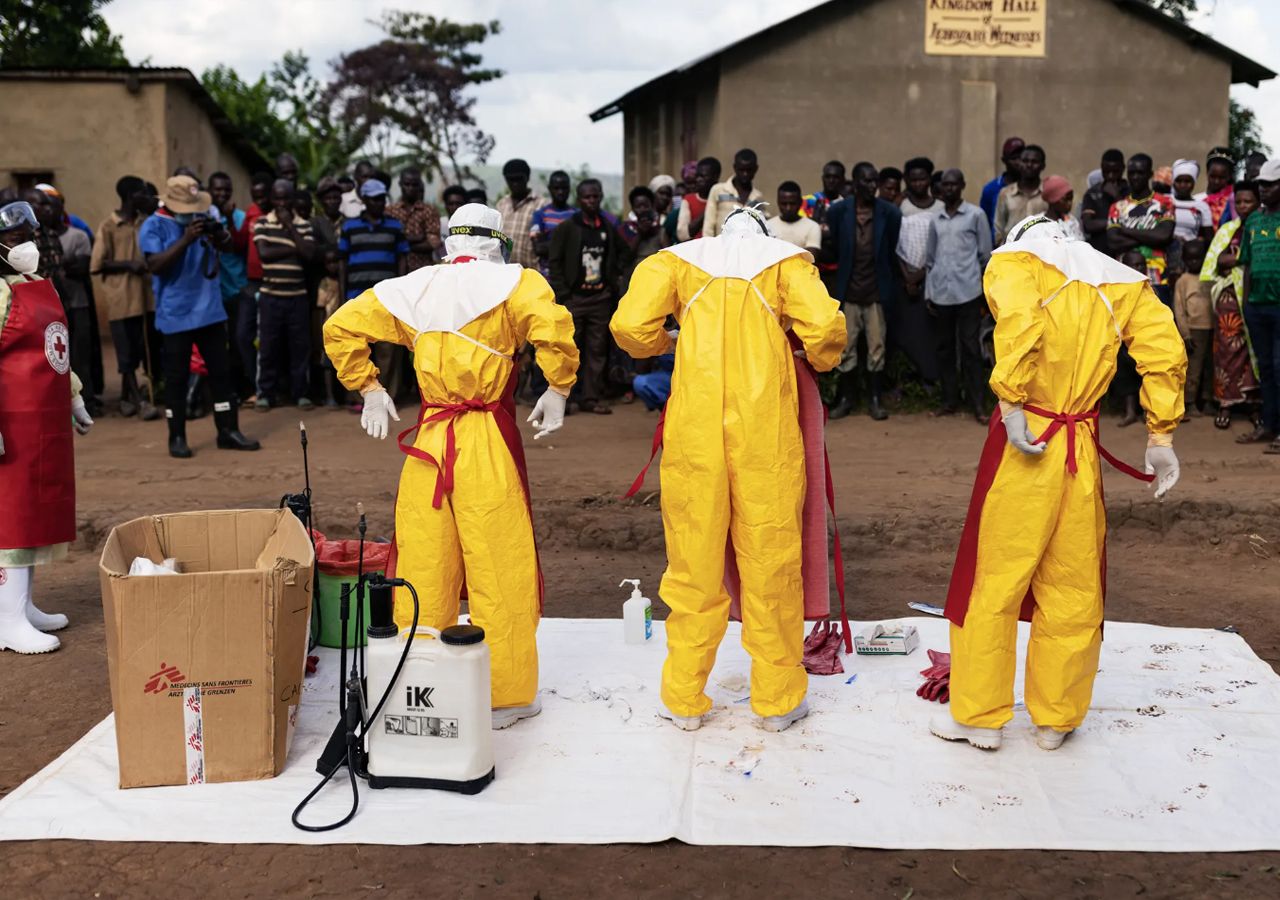
As the world has learned to live with Covid-19, health experts are beginning to prepare for the next potential global threat. In the past two decades, our planet has experienced health crises caused by three major coronaviruses That caused severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), a severe form of pneumonia. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), an acute respiratory disease that primarily affects the upper respiratory tract. And COVID-19 as well 2009 swine flu pandemic.
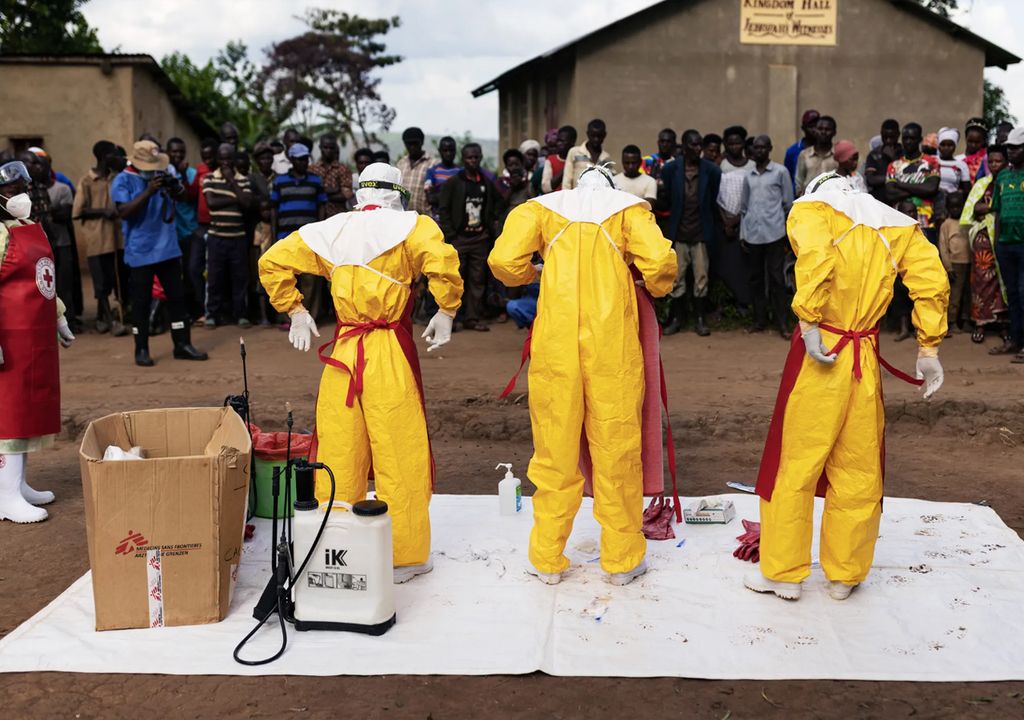

The rapid spread of the H5N1 avian influenza strain is already raising concerns. Although, to date, only a handful of people have been infected and there is no evidence that it has made the leap in human-to-human transmission, skyrocketing rates of transmission among birds and increasing incursions into mammals have raised concerns among the scientific community and governments that the virus may It mutates to facilitate its spread.
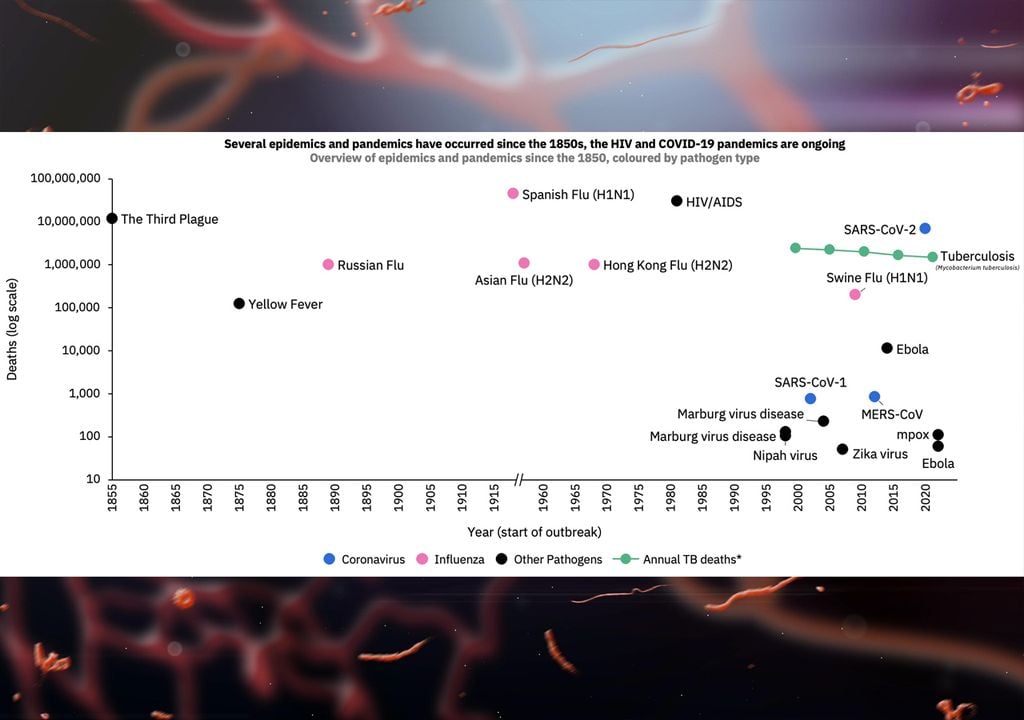
Some high-risk pathogens, such as MERS and Zika, do not have approved vaccines or treatmentsIt is unlikely that health early warning systems will be able to detect a new pandemic in time, highlighting the urgent need for pandemic preparedness measures.
The need to prepare
Although the risk of a new deadly pandemic occurring in the next 10 years is high, the chances of being able to reduce the risks of its spread or deaths are also high.
According to Airfinity, If effective vaccines are developed within 100 days of the discovery of a new pathogen, the probability of a new deadly pandemic drops from 27.5% to 8.1%..
The closest example is how to reduce the death rate during COVID-19, where vaccine efficacy ranges between 50% and 96%Depending on the type of vaccine and doses used.
And how Climate change It will lead many animals to flee their ecosystems in search of more habitable land, The emergence of new diseases that are likely to be transmitted to humans will increase.

Without effective prevention strategies, epidemics will become more frequent, spread faster, and be more deadly.. Its social and economic effects will be devastating on a global scale.
So, We stress the importance of strengthening the resilience of public health systems to disastersparticularly by increasing early warning of acute public health events and Cooperation and synergy between the public and private sectors.

“Wannabe internet buff. Future teen idol. Hardcore zombie guru. Gamer. Avid creator. Entrepreneur. Bacon ninja.”

